反混淆后
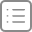
w0是token
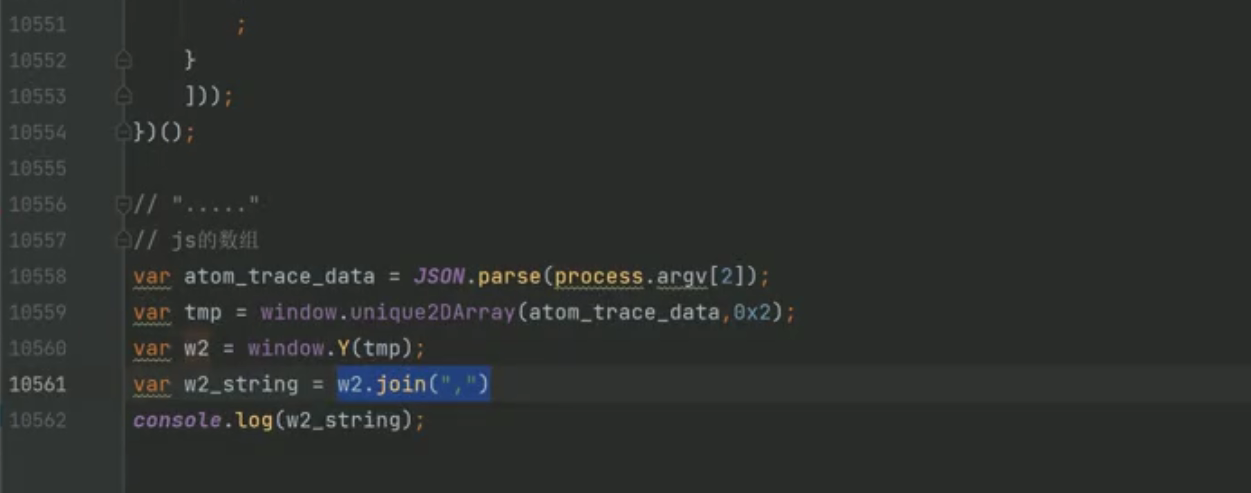
那么w2是什么?

其中,this['atomTraceData']在d分析中得知,是轨迹容器。
那么核心逆向就是
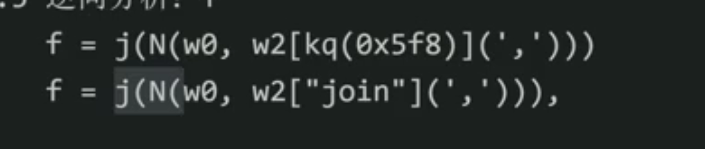
unique2DArray A函数 join拼接 N函数
unique2DArray采用嫁接法,可以直接抠过来。
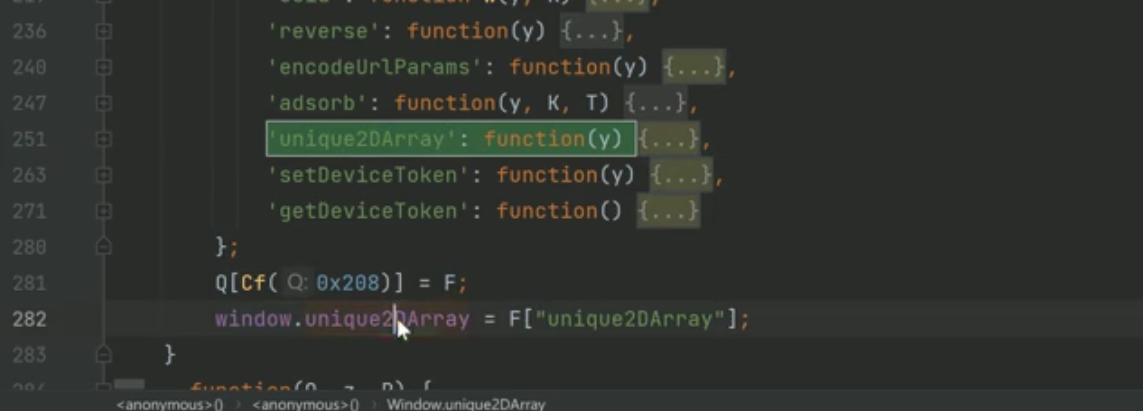
A函数同理:
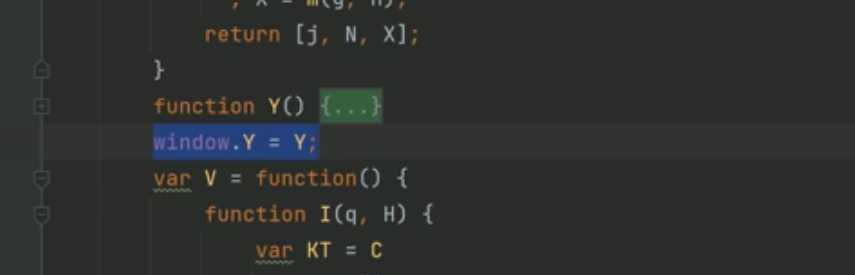
同理,由于这几个函数都在一个js里,那么可以整合
整合代码
import subprocessimport randomimport jsondef N_w8(v1, v2):res = subprocess.check_output(f"node N2.js {v1} {v2}")res = res.decode('utf-8').strip()return resdef A_unique2DArray(v1):res = subprocess.check_output(f"node w2.js {v1}")res = res.decode('utf-8').strip()return resdef j_as_ww(v1):res = subprocess.check_output(f"node j.js {v1}")res = res.decode('utf-8').strip()return resdef run():# 识别滑块的距离x_distance = 100# 背景请求返回的tokenbg_token = "cc7c74c959d842e69aa980a3430b7884"trace_data = []atom_trace_data = []interval_value = random.randint(100, 300)step = 2for i in range(0, x_distance + 1, step):x_value = i + stepif x_value > x_distance:x_value = x_distanceinterval_value += random.randint(10, 20)y_value = random.randint(0, 5)# atom_trace_datachunk_list = [x_value, y_value, interval_value]atom_trace_data.append(chunk_list)# trace_dataline = f"{x_value},{y_value},{interval_value}"line = N_w8(bg_token, line)trace_data.append(line)# print(atom_trace_data)w2_string = A_unique2DArray(json.dumps(atom_trace_data, separators=(',', ':')))f_string = j_as_ww(N_w8(bg_token, w2_string))print(f_string)if __name__ == '__main__':run()