处理d
关系到
D = ?D == T['sample'](this['traceData'], V)// 获取this['traceData']的前50个数据
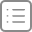
往回翻,反混淆分析鼠标事件函数:
this['traceData']应该就是滑动轨迹,通过鼠标事件读取
var w6 = N(w4, w5 + '');this['traceData'].push(w6)
而w4和w5又从何得来?
var w4 = this[kV(0x2d0)]['state']['token']w5 = [Math[kV(0x17a)](w0[kV(0x466)] < 0x0 ? 0x0 : w0[kV(0x466)]), Math[kV(0x17a)](w0['clientY'] - w0['startY']), T[kV(0x436)]() - w0[kV(0x3da)]];
观察w4,发现是token,解决
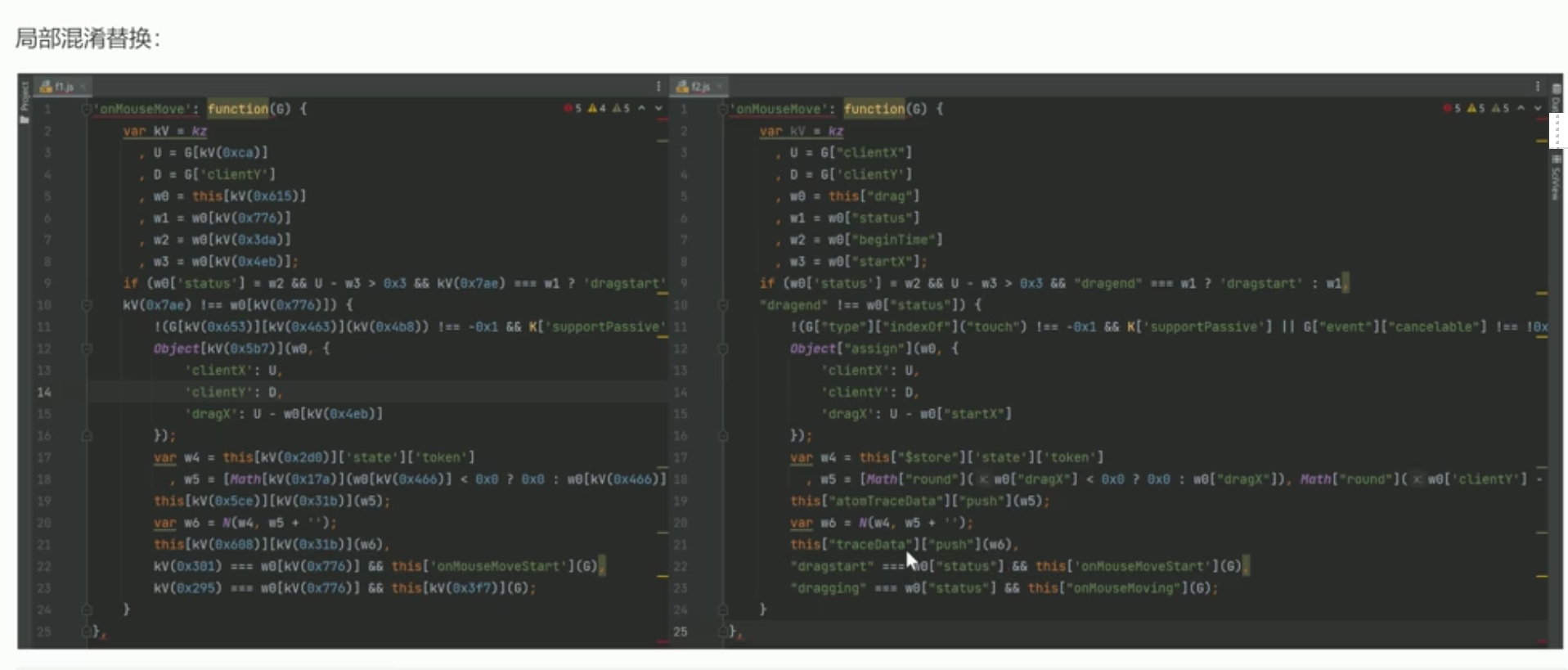
观察w5
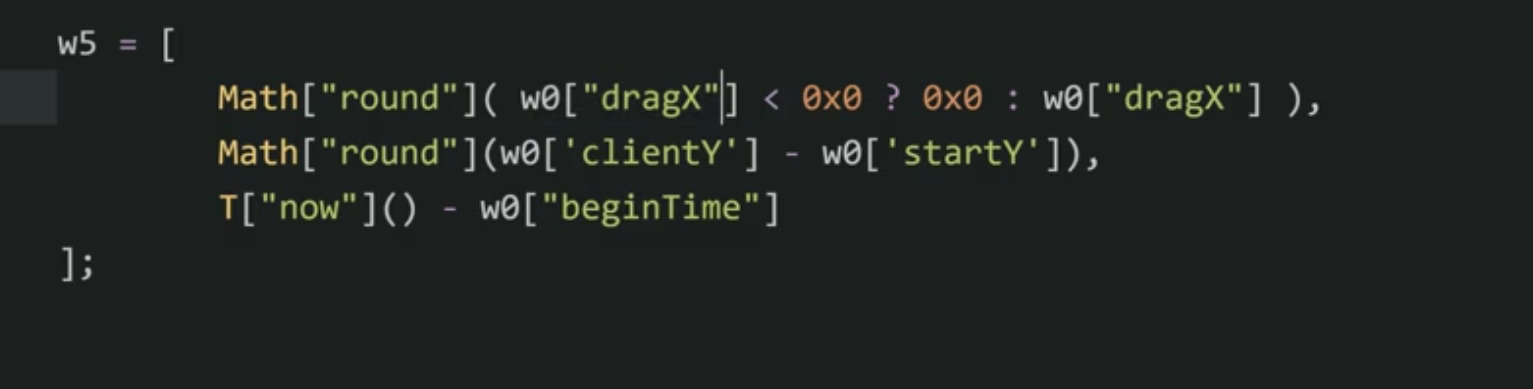
阅读整个分析代码,得知clientX,clientY,dragX,是坐标轨迹计算算法。

然后得知w5的意义:
w5 = [移动的横坐标,移动的纵坐标,当前时间-开始时间]
w6 = N(w4, w5 + '');
接下来是算N了,可以用嫁接法:
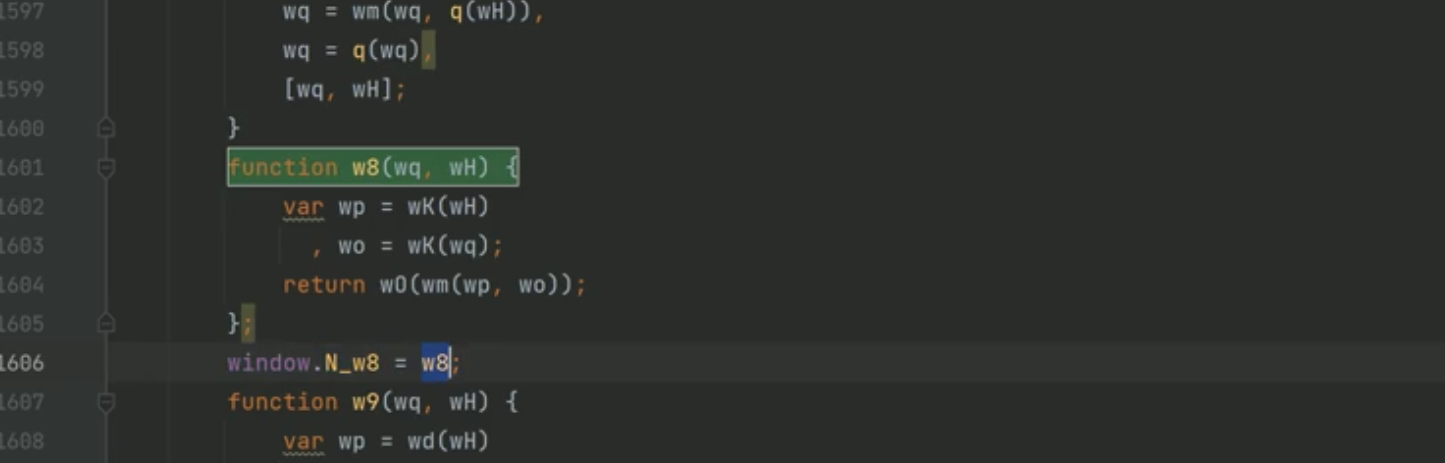
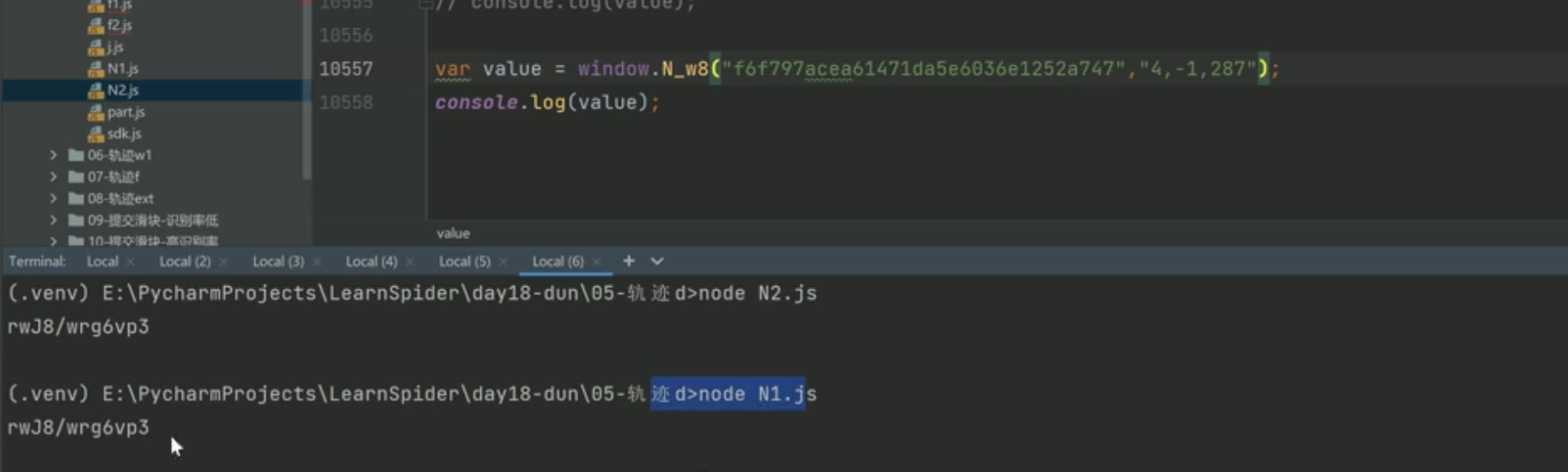
N函数解决后,就可以模拟实现this['traceData']
整合代码:
import subprocessimport randomdef N_w8(v1, v2):res = subprocess.check_output(f"node N1.js {v1} {v2}")res = res.decode('utf-8').strip()return resdef run():# 识别滑块的距离x_distance = 100# 背景请求返回的tokenbg_token = "cc7c74c959d842e69aa980a3430b7884"trace_data = []interval_value = random.randint(100, 300)step = 2for i in range(0, x_distance + 1, step):x_value = i + stepif x_value > x_distance:x_value = x_distanceinterval_value += random.randint(10, 20)y_value = random.randint(0, 5)# trace_dataline = f"{x_value},{y_value},{interval_value}"line = N_w8(bg_token, line)trace_data.append(line)print(trace_data)if __name__ == '__main__':run()
距离D的辅助,还差搞定J函数,发现J函数到处用。
直接上嫁接法:
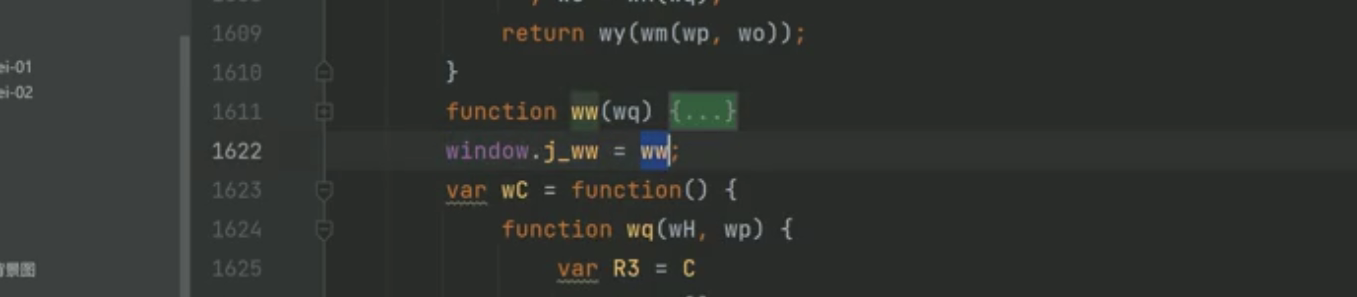
最终整合
import subprocessimport randomdef N_w8(v1, v2):res = subprocess.check_output(f"node N1.js {v1} {v2}")res = res.decode('utf-8').strip()return resdef j_as_ww(v1):res = subprocess.check_output(f"node j.js {v1}")res = res.decode('utf-8').strip()return resdef run():# 识别滑块的距离x_distance = 100# 背景请求返回的tokenbg_token = "cc7c74c959d842e69aa980a3430b7884"trace_data = []interval_value = random.randint(100, 300)step = 2for i in range(0, x_distance + 1, step):x_value = i + stepif x_value > x_distance:x_value = x_distanceinterval_value += random.randint(10, 20)y_value = random.randint(0, 5)# trace_dataline = f"{x_value},{y_value},{interval_value}"line = N_w8(bg_token, line)trace_data.append(line)d_string = j_as_ww(":".join(trace_data[0:50]))print(d_string)if __name__ == '__main__':run()